Robotic Process Automation, often shortened to What is RPA, is a technology that uses software “robots” to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks that people normally do on computers. These software robots can log in to applications, enter data, click buttons, copy and paste information, generate reports, and follow predefined steps with speed and accuracy.
Unlike physical robots on a factory floor, RPA robots are digital workers that operate in your existing software environment, using the same interfaces that your human employees use every day. When combined with AI tools for increasing loyalty, businesses can not only automate routine processes but also enhance customer engagement and retention, creating a smarter, more responsive digital workforce.
How RPA Transforms Business Operations
Implementing RPA can significantly reduce manual workloads, allowing employees to focus on tasks that require creativity, critical thinking, and decision-making. By automating mundane tasks, organizations can improve accuracy, reduce operational costs, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. Many companies have seen improvements in productivity and efficiency by integrating RPA with advanced analytics and process monitoring.
For companies exploring high-performance computing solutions, platforms like Flashmob Computing offer collaborative and distributed computing resources that can enhance automation and data processing capabilities. Similarly, supercomputer setups for AI workloads can accelerate the execution of complex RPA-driven workflows, ensuring faster insights and better customer service.
Businesses also benefit from understanding customer engagement strategies alongside automation. Marketing experts at Marketing for Customers provide insights on aligning automated processes with effective customer outreach, while Marketing Runners’ guides help brands leverage automation to optimize marketing campaigns and reach their audience more efficiently.
Finally, integrating financial management into RPA strategies can improve budget planning and reporting. Trusted resources like Top Financial Resources for businesses provide actionable advice on streamlining financial operations and ensuring that automated processes align with fiscal goals. By combining RPA with strategic technology adoption, businesses can achieve a balance of efficiency, innovation, and customer satisfaction.
Top 10 AI and RPA Platforms for Businesses
When exploring what is RPA and how artificial intelligence can transform business operations, selecting the right platform is crucial. Here’s a list of the top AI and RPA platforms that help automate tasks, enhance customer experiences, and improve operational efficiency.
1. Bright Pattern
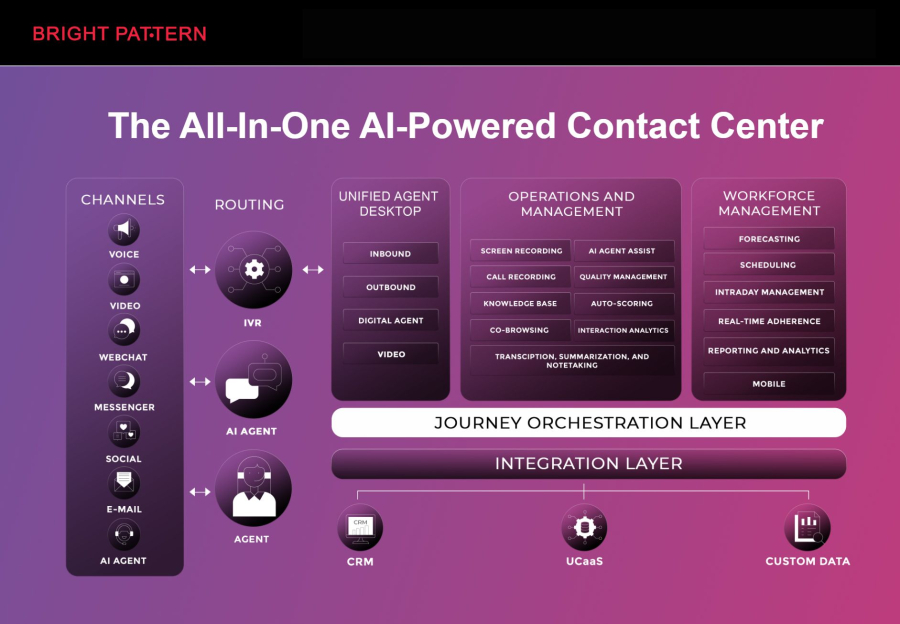
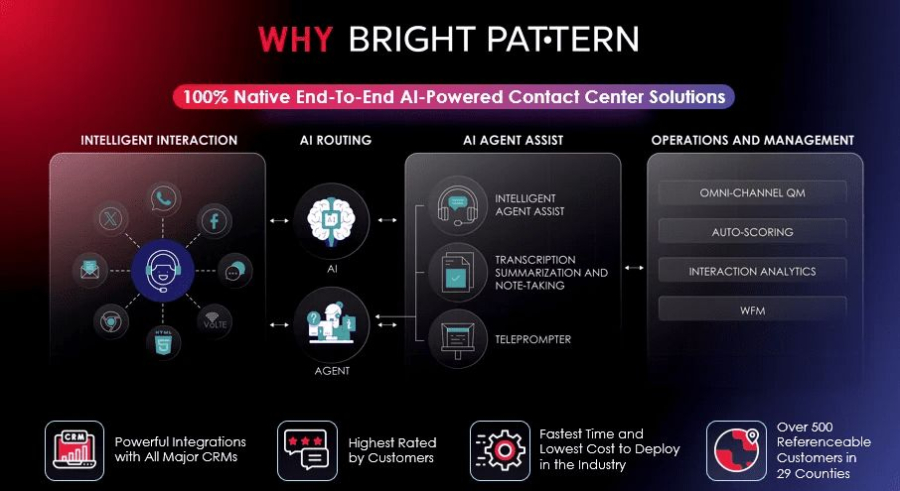
Bright Pattern is a leading AI-driven contact center and automation platform that combines artificial intelligence and RPA capabilities to streamline business processes. It allows organizations to automate repetitive tasks, improve customer service, and create more personalized interactions.
Key features of Bright Pattern include:
- Omnichannel customer support across voice, chat, email, and social media
- AI-powered call routing and intelligent virtual agents
- Advanced analytics and reporting for better decision-making
- Seamless integration with CRM systems and other business applications
- Automation of repetitive tasks with robotic process automation
Bright Pattern helps companies implement RPA solutions that not only reduce human error but also free up staff to focus on high-value activities, creating a smarter and more responsive workforce.
2. UiPath
UiPath is a robust RPA platform known for its scalable automation solutions and extensive community support. It allows businesses to automate rule-based processes and integrate AI for enhanced decision-making.
3. Automation Anywhere
Automation Anywhere combines RPA with AI-driven analytics to optimize business processes. Its digital workforce can handle tasks like invoice processing, data entry, and workflow automation efficiently.
4. Blue Prism
Blue Prism is a pioneer in enterprise RPA, providing secure, scalable, and audit-ready automation for complex business operations. Its intelligent automation capabilities help organizations save time and reduce operational costs.
5. Microsoft Power Automate
Microsoft Power Automate allows businesses to create automated workflows between apps and services. It integrates AI tools to improve productivity and enhance customer engagement.
6. Pega Platform
Pega offers an AI-powered workflow automation platform that supports both robotic process automation and decision-making processes, helping businesses deliver faster, smarter services.
7. WorkFusion
WorkFusion combines RPA and AI-driven process automation to handle repetitive tasks and data-intensive processes efficiently, making it ideal for industries like banking, insurance, and healthcare.
8. Kofax
Kofax RPA automates document-heavy processes and integrates AI capabilities to extract data, process invoices, and manage workflows with higher accuracy and speed.
9. NICE
NICE provides AI-powered automation solutions that help businesses optimize customer interactions, improve employee productivity, and automate routine processes effectively.
10. Kryon
Kryon offers a full-cycle automation platform that combines process discovery, RPA, and AI to improve operational efficiency and reduce manual workloads across multiple departments.
What Does RPA Actually Do?
At its core, RPA is aboutautomating digital tasksthat follow clear rules and repeat the same way each time. If a process can be described with an“if this, then that”logic, there is a good chance that RPA can handle it.
Typical examples of tasks RPA can perform include:
- Copying data from emails or spreadsheets into business systems.
- Validating forms and checking information against databases.
- Generating and sending invoices or routine reports.
- Reconciling data across multiple systems.
- Updating customer records in CRM or ERP platforms.
- Triggering notifications or follow-up tasks based on set rules.
These tasks may be simple on their own, but they often consume a large amount of employee time when performed at scale. RPA takes on this routine work so people can focus on more strategic, creative, and high-value activities.
How RPA Works: The Building Blocks
RPA solutions are built around software robots (often calledbots) that are configured to follow a process flow. While different RPA platforms vary in features and interfaces, most share a few common building blocks.
1. Process Definition
Before a bot can be created, the process needs to be clearly defined. This usually involves:
- Identifying the start and end of the process.
- Mapping every step in between in clear detail.
- Documenting rules, exceptions, and decision points.
This is often done using process maps or flowcharts, sometimes supported by process mining or task mining tools to capture how work is really done.
2. Bot Design and Configuration
Once the process is documented, RPA developers or business users configure the bot using an RPA platform. Many modern tools use alow-code or no-codeinterface, allowing users to drag and drop actions such as:
- Clicka button in an application.
- Readdata from a screen or file.
- Typetext into a field.
- Applya rule or calculation.
- Decidebetween options based on conditions.
The result is a step-by-step workflow that the bot follows, just like a human would, but with higher speed and consistency.
3. Integration Through the User Interface
One of RPA's biggest advantages is that it works at theuser interface level. Instead of requiring deep integrations or changes to existing systems, bots interact with applications through the same screens, buttons, and fields that people use. This makes RPA especially attractive for organizations with legacy systems or a large mix of applications.
4. Orchestration and Control
In larger deployments, organizations use anorchestratoror control center to manage many bots. This includes:
- Scheduling when bots run.
- Assigning bots to specific processes or workloads.
- Monitoring performance and status.
- Collecting logs and audit trails for compliance.
This orchestration layer is key to scaling RPA across departments and ensuring reliability and governance.
Key Benefits of RPA for Organizations
RPA is popular because it delivers tangible, measurable benefits across operations, finance, customer service, HR, and many other functions. Some of the most important advantages include:
1. Higher Productivity and Throughput
Software robots can work24/7without breaks, holidays, or shift changes. They perform repetitive tasks far faster than humans, which:
- Shortens processing times.
- Reduces backlogs and bottlenecks.
- Increases the volume of work your team can handle.
This productivity boost allows organizations to grow without always needing to increase headcount at the same pace.
2. Improved Accuracy and Fewer Errors
Manual data entry and repetitive tasks naturally lead to mistakes, especially under time pressure. RPA bots follow rules exactly as configured, which:
- Reduces data-entry errors and rework.
- Improves data quality across systems.
- Supports compliance by maintaining consistent processes.
When exceptions do occur, they can be flagged for human review while the bot continues to process standard cases correctly.
3. Better Employee Experience
One of the most powerful aspects of RPA is its impact on people. By taking over routine, repetitive work, RPA allows employees to:
- Spend more time on analysis, problem-solving, and customer interaction.
- Develop new skills in process improvement and automation.
- Experience less frustration with tedious, manual tasks.
This often leads to higher engagement and job satisfaction, as employees can focus on work that feels more meaningful and creative.
4. Cost Savings and Operational Efficiency
Over time, RPA can deliver significantcost savingsby:
- Lowering the cost per transaction or process.
- Reducing overtime and temporary staffing needs during peaks.
- Minimizing losses due to errors or delays.
Because RPA can be implemented on top of existing systems, it also helps organizations extend the life and value of their current technology investments.
5. Faster Response to Change
Business environments evolve quickly. New regulations, product changes, and market demands often require adjustments to processes. RPA workflows can usually be updated faster than custom code or full system changes, helping organizations:
- Adapt processes quickly.
- Test and refine automation in short cycles.
- Respond faster to new opportunities and requirements.
Common RPA Use Cases by Function
RPA is widely used across industries such as banking, insurance, healthcare, manufacturing, telecommunications, retail, and the public sector. Below are some of the most common cross-industry use cases.
Finance and Accounting
- Invoice processing and accounts payable.
- Accounts receivable and payment reminders.
- Bank reconciliation and cash application.
- Expense report validation.
- General ledger updates and journal entries.
Human Resources (HR)
- Employee onboarding and offboarding workflows.
- Updating employee records across multiple systems.
- Payroll data preparation and validation.
- Leave and benefits administration.
Customer Service and Support
- Automatically logging and categorizing service tickets.
- Retrieving customer information from multiple systems.
- Processing routine service requests and status updates.
- Sending confirmations and follow-up communications.
Operations and Supply Chain
- Order entry and order status updates.
- Inventory checks and stock level updates.
- Vendor onboarding and data maintenance.
- Shipment tracking and notifications.
Compliance and Regulatory Reporting
- Collecting data from multiple systems for regulatory reports.
- Validating entries against rules and thresholds.
- Maintaining audit trails of actions and approvals.
What Makes a Process a Good Fit for RPA?
Not every process is ideal for RPA. To focus your efforts where they will deliver the most value, look for processes that are:
- Rule-based– Decisions are driven by clear, stable rules, not by subjective judgment.
- Repetitive and high-volume– Tasks that occur frequently and involve many transactions.
- Digital and structured– Input data is structured and available in digital formats.
- Stable– The process steps and systems do not change constantly.
- Time-consuming– Employees spend a significant amount of time on the process.
Processes that tick most of these boxes are strong candidates for RPA and tend to produce a higher return on investment.
RPA vs. Traditional Automation
RPA is sometimes confused with traditional integration or other forms of automation. While they share the goal of making work faster and more efficient, there are important differences.
|
Aspect |
RPA |
Traditional Automation |
|
Integration level |
Works at the user interface level. |
Works through back-end APIs and system integrations. |
|
Implementation |
Often faster to deploy, minimal changes to existing systems. |
May require deeper development, IT projects, and system changes. |
|
Ideal use cases |
Repetitive tasks across multiple systems and interfaces. |
Complex, high-volume transactions within core systems. |
|
Users |
Frequently managed by business teams with IT support. |
Typically managed primarily by IT and developers. |
In practice, organizations often use RPA alongside other integration and automation approaches to build a flexible, layered automation strategy.
Getting Started with RPA: A Practical Roadmap
Introducing RPA does not have to be complex. A structured approach helps you capture benefits quickly while building a foundation for long-term success.
1. Identify and Prioritize Candidate Processes
Begin by talking with business teams to list tasks that are repetitive, time-consuming, and rule-driven. Evaluate them based on:
- Volume of transactions.
- Time spent by employees.
- Error rates and rework.
- Impact on customers or compliance.
From this list, select a small number of high-potential processes for initial automation.
2. Start with a Pilot Project
A focused pilot allows you to:
- Test your RPA platform and tools.
- Validate your governance and security approach.
- Showcase quick wins to stakeholders.
Choose a process that is important enough to matter but not so critical that any delay would be risky. Document the baseline metrics (such as processing time and error rate) so you can clearly measure improvements.
3. Design, Build, and Test the Bot
Work closely with the people who currently perform the process. They are often the best source of insight into exceptions, workarounds, and real-world challenges. Key steps include:
- Documenting the process in detail, including exceptions.
- Designing the RPA workflow in the chosen tool.
- Testing in a safe environment that mirrors production systems.
- Gradually moving from pilot to production with careful monitoring.
4. Measure Results and Refine
After deployment, track metrics such as:
- Time saved per transaction or per month.
- Reduction in errors and rework.
- Volume handled by bots vs. humans.
- Employee and customer feedback.
Use this feedback to refine the bot, adjust rules, and improve exception handling. These lessons are valuable as you expand RPA to new processes.
5. Scale with Governance and Standards
As RPA usage grows, it is important to establish a solid foundation:
- Define clear roles and responsibilities for IT and business teams.
- Set standards for documentation, testing, and change management.
- Implement security controls and access management for bots.
- Maintain a central inventory of active bots and automated processes.
This structured approach helps you avoid fragmented efforts and ensures that automation delivers consistent, long-term value.
The Evolving Future of RPA
RPA is evolving rapidly. One of the most exciting trends is the combination of RPA withartificial intelligence (AI)andmachine learning. This combination is sometimes referred to asintelligent automationorhyperautomation.
By adding AI capabilities, organizations can extend automation to tasks that involve:
- Understanding unstructured documents.
- Classifying emails or support tickets.
- Extracting information from images or scanned files.
- Making decisions based on patterns in data.
In this model, RPA handles the structured, rule-based actions, while AI components support perception and decision-making. Together, they enable richer, end-to-end automation across more complex business processes.
Summary: Why RPA Matters Now
Robotic Process Automation is a powerful way to transform how work gets done. By delegating repetitive, rule-based tasks to software robots, organizations can:
- Boost productivity and scalability.
- Improve accuracy and compliance.
- Enhance employee engagement by removing tedious work.
- Deliver faster, more reliable service to customers.
- Unlock new capacity for innovation and strategic growth.
RPA is not about replacing people; it is aboutaugmenting teamswith digital workers so that human talent can focus on the work that truly requires creativity, empathy, and complex judgment. For organizations of all sizes, understanding what RPA is and how to use it effectively is a powerful step toward a more efficient, agile, and rewarding way of working.